SHOULDER BOLTS MANUFACTURER IN CHINA
Ningbo Teng Qi Fasteners Co., Ltd specialized in producing shoulder bolts. Shoulder bolts, also known as shoulder screws or stripper bolts, are fasteners designed with a cylindrical shoulder beneath the head. This shoulder acts as a precise pivot point or spacer, allowing for rotational movement or precise spacing between components. The threaded portion of the bolt can be used to secure the bolt in place. These bolts are often used in applications where accurate alignment or spacing is important, such as in machinery, electronics, and automotive assemblies. The shoulder bolts have high hardness, good toughness, excellent wear resistance and heat resistance, and is suitable for precision molds, which can significantly improve its service life, especially the thermal deformation of precision molds has been effectively controlled, and is suitable for molds in high temperature working environment.
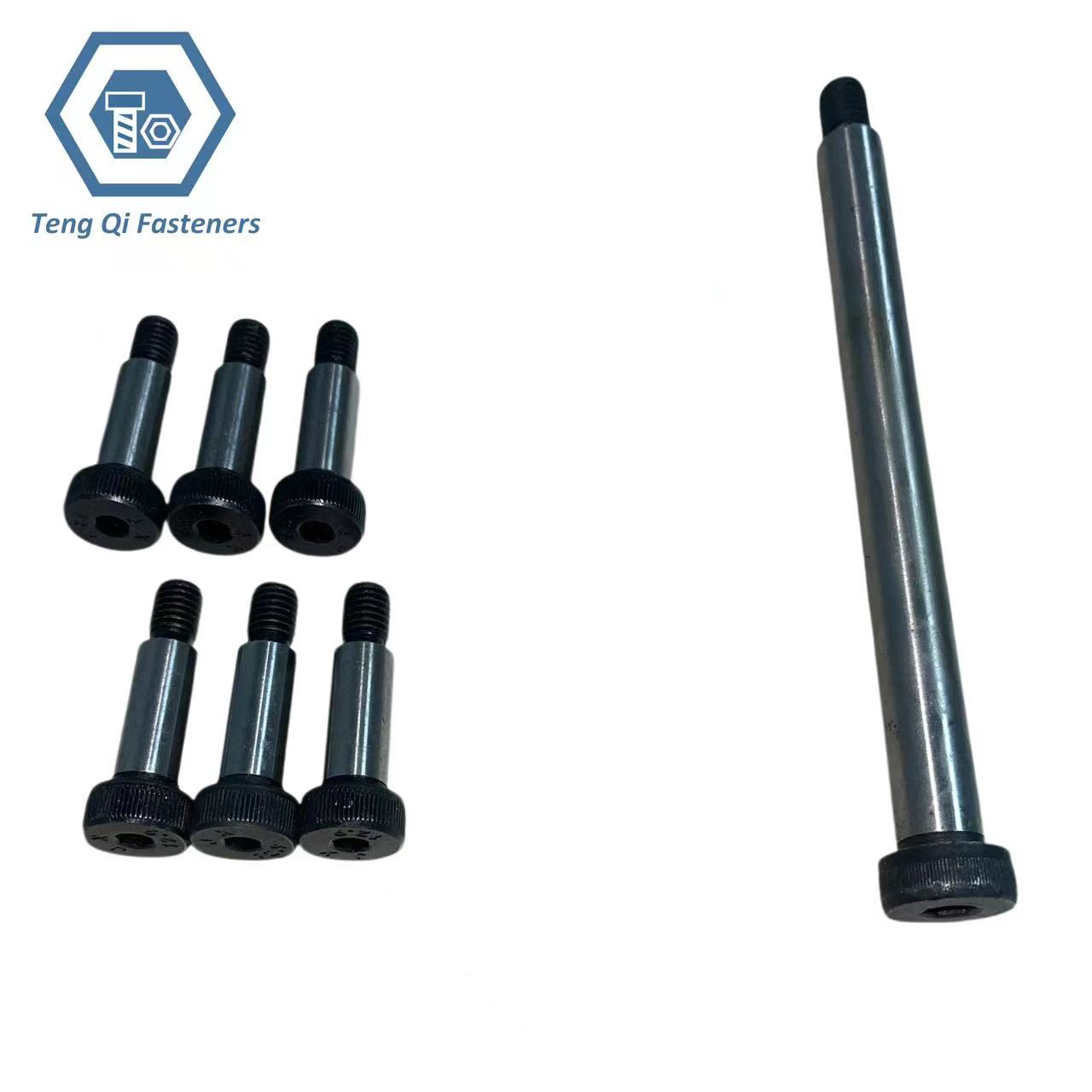

Specification of shoulder bolt:
The specifications of shoulder bolts can vary depending on the manufacturer and the specific application. However, some common specifications include:
| Product name: | Shoulder Bolts |
|---|---|
| Diameter | Metric: M2-M48 Imperial:1/32"-2" |
| Thread Tolerance | 6g |
| Length | Metric: Up to 200mm Imperial: Up to 8" |
| Head Type | Hexagon Socket head/Hex head/slotted Head |
| Mechanical property | Alloy Steel: class12.9 (Due to structural reasons, these screws cannot withstand tensile tests, but the other performance requirements specified by ISO 898-1 for class 12.9 should be met.) |
| Material | Alloy Steel/Stainless steel |
| Shoulder Parts | Surface roughness Ra=0.8μm (ISO 1302), applicable only before plating |
| Surface treatment | Black Oxide Coating/Passive/Zinc Plated |
| Application | The shoulder bolt is used in conjunction with the bolt tie rod, mainly used for controlling the opening stroke between the fixed die seat plate, the runner push plate and the fixed die template in the three-plate die. |
Locking may occur when using the plug screw, because the plug screw itself has a good anti-corrosion performance, but when its surface is damaged, the metal surface of the plug screw will form a protective film to prevent the screw from corroding again. When the stainless steel fasteners are locked, the pressure and heat generated between the teeth will make this protective film lose its function, causing obstruction between the threads, and slowly resulting in the phenomenon of locking.
Choose the right shoulder bolts:
1 Before using the shoulder screw to confirm the mechanical properties of the screw meet their needs, such as the tensile performance of the screw and the guaranteed load of the nut. The size of the screw should be confirmed, and it is better to expose 2 or so teeth after tightening.
2 Confirm that the thread complies thread gauge, between the threads to keep clean can not have debris, because debris may lead to locking phenomenon.
3. Lubricate the plug screws before use, which can prevent the screws from locking.
Production process:
The requirement of dimension tolerance is precision and surface finish is high for shoulder parts of shoulder bolts. Compared with regular bolts, the shoulder parts needs to be grinned to achieve the required finish after thread rolling.
- Prepare material for wire drawing and annealing
- Cold heading forming
- CNC turning
- Threading Rolling
- Heat treatment
- Black Oxidation
- Grinding the shoulder parts
- Packing
Quality control:
| Control Method | Detail |
|---|---|
| Material Inspection: | Verify the material's composition, heat treatment, and quality upon receipt. Conduct metallurgical analysis to ensure the material properties meet the standards. |
| Process Control: | Implement strict process control measures for heat treatment, machining, threading, and any other manufacturing steps. Maintain consistent process parameters to ensure uniform quality. |
| Inspection Points: | Introduce inspection points at various stages of manufacturing to check for defects, dimensions, and quality. Inspect threading, dimensions, surface finish, and other critical parameters. |
| Sampling and Testing: | Regularly sample products for testing, such as tensile testing, hardness testing, and metallurgical analysis, to ensure they meet the required specifications. |
| Thread Inspection: | Thoroughly inspect threading using proper thread gauges to ensure accurate dimensions and fit with mating components. |
| Traceability: | Implement a traceability system to track each fasteners journey from raw material to final product. This aids in accountability and recalls if necessary. |